Exploring the Benefits of Rhodiola Rosea: An Adaptogen for Athletes
Rhodiola rosea, commonly known as golden root or Arctic root, is a hardy perennial herb that thrives in high-altitude regions across Europe and Asia. This plant is recognized not only for its traditional medicinal applications, including treating fatigue and anxiety but also for its potential adaptogenic properties, aimed at enhancing both physical and mental performance. Investigations into its bioactive compounds—such as rosavin and salidroside—have revealed promising antiviral and antibacterial activities as well. With a growing interest in natural remedies for athletic performance and recovery, Rhodiola rosea has emerged as a focal point for research, particularly concerning its effectiveness in preventing infections in athletes following strenuous activities.
Understanding Adaptogen and Ergogen Effects
The adaptogenic properties of Rhodiola rosea suggest it may play a crucial role in helping the body adapt to stressors, whether they be physical, emotional, or environmental. Adaptogens are substances that can enhance the body’s resilience to stress and improve overall wellness. In this context, research indicates that Rhodiola rosea benefitted endurance athletes, although previous findings from studies like Shanely et al. demonstrated no significant reduction in muscle damage or inflammation after intense exercise when supplemented with this herb. Nevertheless, Rhodiola rosea‘s potential to combat oxidative stress—a common consequence of rigorous training—offers an intriguing avenue for further research into its benefits for athletes.
Antiviral Properties against Pathogens
Emerging studies have indicated that Rhodiola rosea can inhibit viral activity, contributing to its appeal among athletes. Various bioactive constituents have demonstrated the ability to modulate immune responses and potentially offer protective effects against viral infections, such as influenza and coxsackievirus B3. The plant has been reported to bolster the innate immune response by enhancing the expression of antiviral cytokines, which are crucial for combating viral replication. These findings are particularly relevant, as endurance athletes often experience transient immune dysfunction following prolonged exercise, making them more susceptible to infections.
Research on Athletes: Methodology and Findings
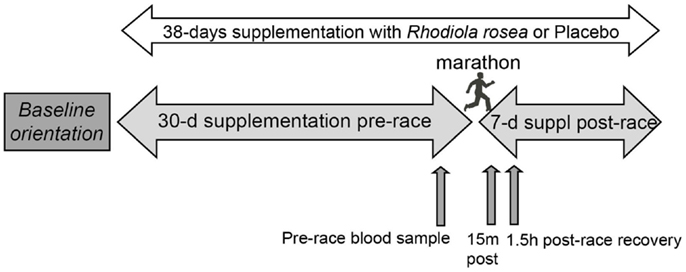
In an effort to rigorously analyze Rhodiola rosea’s efficacy, researchers conducted a study involving trained runners who ingested either Rhodiola rosea or a placebo for 30 days leading up to a competitive marathon. Blood samples were analyzed to evaluate the serum’s antiviral and antibacterial activities pre- and post-race. Although no significant effect was observed on bacterial growth, the study reported a suppression of virus replication in those taking Rhodiola rosea compared to placebo, indicating a potential advantage in enhancing immune function under stress derived from extreme exertion.
Effects on Bacterial Growth
Interestingly, despite its antiviral efficacy, the same study revealed that Rhodiola rosea supplementation did not significantly inhibit the growth of well-known pathogens like Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Instead, post-marathon assessments indicated an exercise-induced increase in both bacterial strains, suggesting that intense exercise may compromise gut health or immunity. This outcome necessitates further investigation into the dual nature of Rhodiola rosea—not only as a potential antiviral agent but also in relation to bacterial infections.
Potential Mechanisms Behind Immune Benefits
Several mechanisms could explain the immune-boosting effects of Rhodiola rosea. Research suggests that the constituents of this herb may influence oxidative stress levels, which is crucial in athletes who often experience increased levels post-exercise. Additionally, Rhodiola rosea may promote cellular processes that both enhance immune responsiveness and mitigate the damaging effects of oxidative stress. Future studies aim to clarify how these molecular pathways operate and whether Rhodiola rosea could be essential in preventing viral infections in athletes.
The Future of Rhodiola Rosea in Sports Nutrition
As athletes increasingly turn to natural supplements, Rhodiola rosea stands out as a promising candidate for enhancing performance and recovery. The evidence thus far suggests that while it may not significantly affect bacterial growth, its antiviral capacities could be invaluable in safeguarding an athlete’s health during strenuous training periods. Continued exploration of Rhodiola rosea could potentially inform guidelines for effective dietary supplementation in the athletic community, ultimately contributing to longevity in sports performance. For further insights, exploring detailed research studies and reviews can provide comprehensive knowledge on this adaptogen’s benefits (PubMed).